I18n with Angular Translate
Your application could be required to support multi-languages. There are a few solutions to support i18n in Angular applications.Angular translate is one of the most populars.
Install angular translate packages.
npm install --save angular-translate angular-translate-storage-cookie angular-translate-storage-local
//...
import 'angular-translate';
import 'angular-translate-storage-cookie';
import 'angular-translate-storage-local';
//...
const requires = [
'pascalprecht.translate',
//...
$translateProvider in app.config.js file.import en from './i18n.en.json';
import zh from './i18n.zh.json';
function AppConfig(/.../, $translateProvider){
//...
// Adding a translation table for the English language
$translateProvider.translations('en', en);
// Adding a translation table for the Chinese language
$translateProvider.translations('zh', zh);
// Tell the module what language to use by default
$translateProvider.preferredLanguage('en');
// Tell the module to store the language in the local storage
$translateProvider.useLocalStorage();
}
Install json-loader.
npm install --save json-loader
{ test: /\.json$/, loader: 'json' },
i18n.en.json:
{
"posts": "Posts",
"new-post": "New Post"
}
{
"posts": "博文",
"new-post": "新建博文"
}
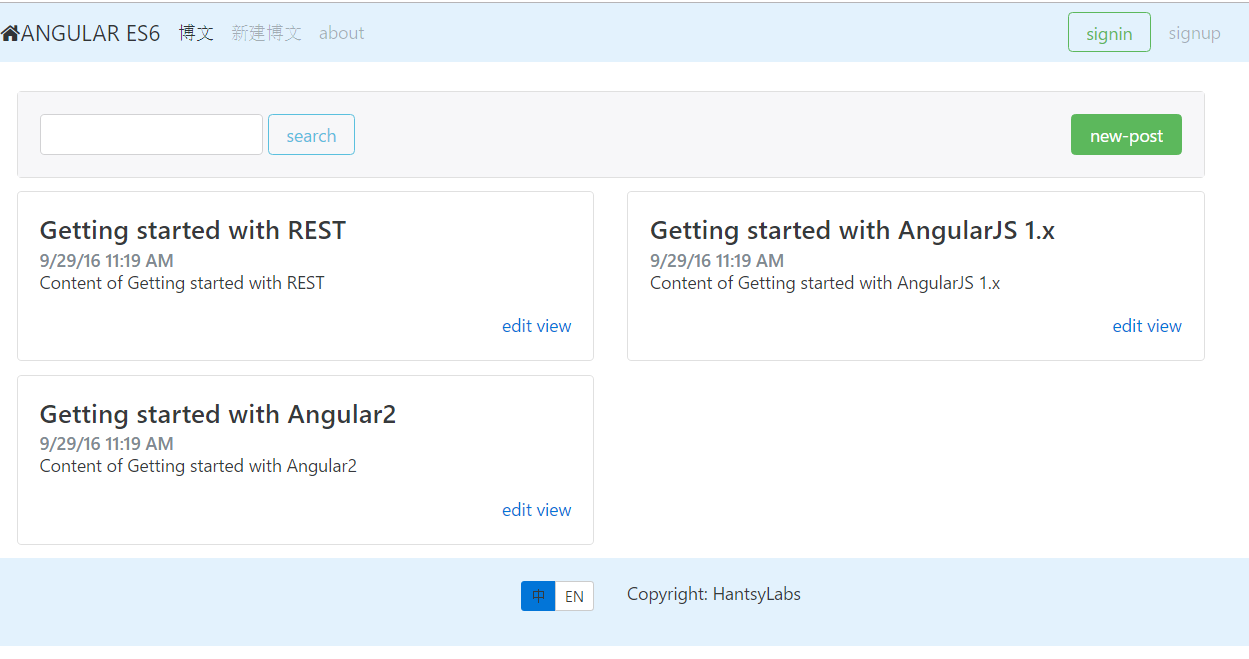
<li class="nav-item" ui-sref-active="active"><a class="nav-link" href="#" ui-sref="app.posts">{{'posts'|translate}}</a></li>
<li class="nav-item" ui-sref-active="active"><a class="nav-link" href="#" ui-sref="app.new-post">{{'new-post'|translate}}</a></li>
<li class="nav-item" ui-sref-active="active"><a class="nav-link" href="#" ui-sref="app.about">{{'about'|translate}}</a></li>
translate filter to translate the text in links.Now run the application via executing
gulp serve in the project root folder.
As you see the posts, new-post in the navbar are replaced with the texts in our i18n.json for English language. But we have not set about there, it displays the original text, and does not indicate what we had omitted.
There are some approaches to notify developers.
Install angular-translate-handler-log which is an extension of angular-translate.
npm install --save angular-translate-handler-log
import 'angular-translate-handler-log';
app.config.js file.$translateProvider.useMissingTranslationHandlerLog();

And you can also handle the exception when the item to be translated is not found.
Define an angular factory.
.factory('customTranslationHandler', function () {
return function (translationID) {
// return the following text as a translation 'result' - this will be
// displayed instead of the language key.
return '[' + translationID + ']';
};
})
useMissingTranslationHandlerLog. $translateProvider.useMissingTranslationHandler('customTranslationHandler');
$translate service to change language and set language.In footer.controller.js, add methods:
setLanguage(key) {
this._$translate.use(key);
}
isLanguage(key) {
return key===this._$translate.use();
}
<div class="btn-group btn-group-sm" role="group">
<a class="btn" ng-class="($ctrl.isLanguage('zh')) ? 'btn-primary' : 'btn-secondary'" ng-click="$ctrl.setLanguage('zh')">中</a>
<a class="btn" ng-class="($ctrl.isLanguage('en')) ? 'btn-primary' : 'btn-secondary'" ng-click="$ctrl.setLanguage('en')">EN</a>
</div>
More about
$translate, check official Angular translate docs .Angular translate support variables in translation text.
For example, translate the welcome info for signin page.
"welcome-back":"Welcome back,{{name}}"
this._toastr.success(this._$translate.instant('welcome-back', {
name: this.data.username
}));
Just install
angular-translate-interpolation-messageformat which bridges angular translate with messageformat:npm install --save angular-translate-interpolation-messageformat
app.config.js:$translateProvider.useMessageFormatInterpolation();
评论